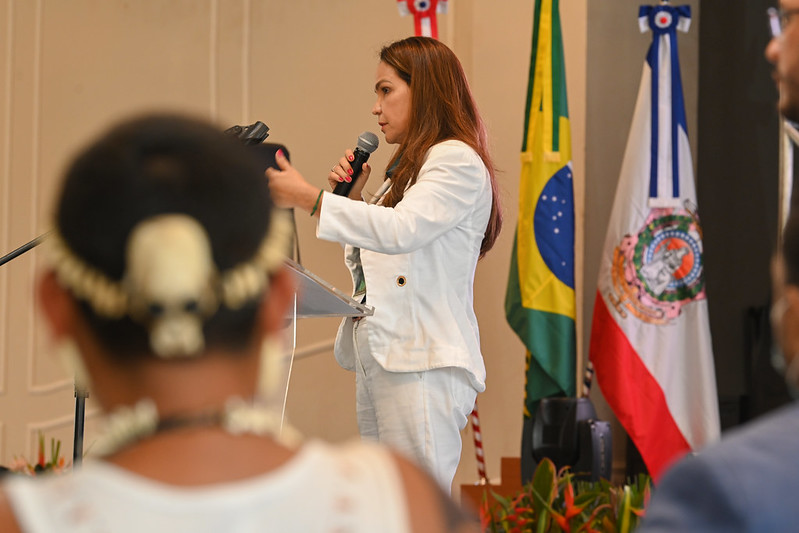
Lei que cria a “Semana Cultural dos Povos Indígenas” foi sancionada em Rondônia
Semana Cultural dos Povos Indígenas que abordará a realidade dos povos originários

Nesta semana foi sancionada pelo governo de Rondônia, a Lei n° 5.452/22 aprovada na Assembleia Legislativa do Estado – ALE/RO, que cria a Semana Cultural dos Povos Indígenas. A iniciativa regulamenta em seus oito artigos, a conscientização quanto à importância da cultura e a preservação da memória dos povos que originariamente habitam o Estado de Rondônia.
A diversidade de povos indígenas presentes em toda a região Norte do Brasil e em grande número no Estado de Rondônia tem levado as autoridades locais a potencializarem políticas para desenvolver este seguimento da sociedade brasileira. Em apontamentos de lideranças indígenas, os últimos quatro anos têm sido proveitosos em ações quanto aos cumprimentos de objetivos constitucionais, em especial, o Inciso IV do Artigo 3° – promover o bem de todos, sem preconceitos de origem, raça, sexo, cor, idade e quaisquer outras formas de discriminação.
A legislação que cria a agenda de debates sobre a valorização do indígena, marca a entrada no Calendário Oficial do Estado de Rondônia das comemorações, que anualmente acontecerão entre os dias 18 a 21 de abril.
As mais de 54 etnias de Rondônia, segundo dados da Secretaria de Estado do Desenvolvimento Ambiental – Sedam, que têm usufruto das terras da União dentro das divisas rondonienses, para desenvolverem atividades econômicas com sustentabilidade têm se beneficiado de políticas do órgão. Uma das articuladoras é a Coordenadoria de Povos Indígenas – Copin, que submete propostas e projetos que possam garantir a geração de renda de forma sustentável nos territórios indígenas.
A inferência que a Semana Cultural dos Povos Indígenas faz em sua Lei, referente à desconstrução destes povos, é para o professor e pesquisador Alécio Valois, coordenador de Patrimônio do Estado de Rondônia – Sejucel, a síntese da motivação pública de defesa deste seguimento de população. “Estes dias de eventos anuais serão uma oportunidade para os indígenas falarem sobre sua realidade, além disso, professores e pesquisadores de diversas etnias compartilharão suas experiências”, pontuou Alécio.
PROCESSO HISTÓRICO
A desconstrução da visão preconceituosa frente à temática indígena, segundo o coordenador da Sejucel, só pode ter êxito se houver uma um olhar de todos os cidadãos sobre a realidade. “Somente assim poderemos ter uma sociedade mais tolerante, mais solidária e mais fraternal ”, contribuiu Alécio Valois.
O coordenador explica, ainda, a face de interculturalidade dos eventos oficiais da semana, de modo que profissionais de diversas áreas de conhecimento, bem como história, direito, entre outros, podem pormenorizar a visão de quem tem raízes indígenas e desenvolve suas atividades junto à sociedade. “Este estímulo cria uma relação intercultural que incentiva não indígenas a visitarem reservas indígenas sem a visão do índio do ano de 2022, não do índio de 1.500”, reconheceu Valois.
IDENTIDADE
Em comparação aos pesos e medidas nos quais a sociedade brasileira acostumou-se, Alécio relacionou o preconceito, no qual os grupos de Movimentos dos Sem Terra – MST sofrem por invadirem propriedades privadas, porém não há o mesmo rigor quanto sociedade frente à defesa indigenista. “Parte de nossos ancestrais, não indígenas invadiram terras que já eram ocupadas, então somos sem terra também, mas a maioria da sociedade não se olha como tal”, salientou.
O representante e conselheiro titular do Setorial Indígena de Rondônia, Welington R. Cinta Larga, emocionou-se ao comemorar a quebra de paradigma que a nova Lei vem proporcionar. “É gratificante saber que vamos ter a oportunidade de mostrar nossa cultura, nossa arte e mostrar para indígenas e não indígenas que nós estamos aqui”, declarou. Para ele, se a legislação permanecer será um fortalecimento à origem e cultura do País.
A Constituição Federal de 1988 possui o Capítulo VIII, exclusivo com dois artigos que versam sobre a defesa dos índios e seu reconhecimento apresentando uma organização social, costumes, línguas, crenças e tradições. No Censo do IBGE de 2010, o Brasil possuía 817.963 índios, dos quais aproximadamente 62% vivem em áreas rurais.
FONTE:
Seminário 20 anos da Política de Cooficialização de Línguas por Municípios Brasileiros
Uso de cartazes sobre audiências de custódia traduzidos para línguas indígenas é tema de painel apresentado por juíza do TJAM na 1.ª Conferência Amazônica do Clima e do Meio Ambiente
Coordenadora das Audiências de Custódia, a juíza André Jane falou sobre a iniciativa, resultado de parceria que envolve o CNJ, o Escritório das Nações Unidas sobre Doenças e Crime, a Esmam, o TJAM e organizações indígenas.
A experiência do projeto de tradução de cartazes desenvolvido pela Escola Superior da Magistratura do Amazonas (Esmam), em parceria com o Conselho Nacional de Justiça (CNJ) junto a povos indígenas, dentro do “Programa Fazendo Justiça”, foi compartilhada nesta sexta-feira (18/11) em um dos painéis do segundo e último dia da “1ª Conferência Amazônica do Clima e do Meio Ambiente”. O evento é organizado pela Escola Nacional de Formação e Aperfeiçoamento de Magistrados (Enfam) e Esmam tendo como local o Salão Rio Solimões do Palácio Rio Negro.
A apresentação do projeto ocorreu dentro do Painel 1 – “Acesso intercultural à justiça aos povos da floresta: garantindo informação sobre Audiências de Custódia em línguas indígenas no Amazonas” -, com explanação realizada pela juíza de Direito da 5.ª Vara Criminal de Manaus e coordenadora da Coordenadoria das Audiências de Custódia do Tribunal de Justiça do Amazonas, magistrada Andrea Jane Silva de Medeiros.
A comunicação intercultural acontece através de cartazes com uma série de materiais informativos sobre audiências de custódia traduzidos para as respectivas línguas indígenas, baseado na cartilha divulgada em 2021 pelo CNJ para a qualificação das audiências, conforme informou Andrea Jane, que é graduada pela Ufam (1994) e pós-graduada em Direito Penal e Processo Penal pela mesma instituição de ensino superior, e em Direito Eleitoral pela Universidade do Estado do Amazonas (UEA).
“Nós apresentamos hoje uma das ações resultantes da parceria entre o Tribunal de Justiça, a Escola da Magistratura do Amazonas e o Conselho Nacional de Justiça (CNJ), no âmbito do ‘Programa Fazendo Justiça’, do CNJ. Trata-se de um projeto de tradução de cartazes sobre audiências de custódia para as línguas indígenas do Alto Solimões, na língua Tikuna, e Vale do Javari, para as línguas Kanamari, Matis e Marubo. O projeto-piloto foi realizado através do CNJ em abril deste ano, em São Gabriel da Cachoeira, no Alto Rio Negro, onde foi traduzido também para três línguas. E o Tribunal de Justiça entrou com apoio, diferentemente deste projeto agora, em que ele toma à frente e passa a institucionalizar essa prática”, explicou ela, frisando que, a partir do protagonismo indígena, o CNJ publicou a Resolução CNJ n.º 287/2019, que estabelece procedimentos voltados para a garantia dos Direitos Humanos do indígena que responde a processos criminais.
A partir do projeto-piloto em São Gabriel da Cachoeira, disse a juíza e coordenadora, o Tribunal do Amazonas, que figurava como apoio, passou através da Coordenadoria das Audiências de Custódia, e com a parceria com a Esmam, a institucionalizar a prática com a escolha da região do Alto Solimões e do Vale do Javari. “E a partir desse projeto de institucionalização da tradução dos cartazes para línguas indígenas, foram realizadas inúmeras reuniões e encontros in loco em Benjamin Constant, Tabatinga e Atalaia do Norte, que contaram com a participação do Grupo de Monitoramento Carcerário, com a presença do desembargador Elci Simões, da Coordenadoria das Audiências de Custódia do Amazonas, da Esmam e com as organizações indígenas e indigenistas daquela região. E dessas reuniões chegou-se à necessidade de tradução dos cartazes contendo as informações das audiências de custódia para as línguas indígenas do Alto Solimões. Foi uma escolha natural, mas os indígenas da região foram ouvidos”, informou a magistrada.
A magistrada frisou que, em 2022, o Conselho Nacional de Justiça publicou a Resolução n.º 254, que estabelece diretrizes e procedimentos para efetivar a garantia do direito ao acesso ao Judiciário da pessoa e dos povos indígenas. No âmbito do Tribunal de Justiça do Amazonas, com a importante parceria da Esmam, que encampou, na pessoa do desembargador João de Jesus Abdala Simões, esse projeto trata, em sua essência, da promoção e garantia desse direito. Um acesso intercultural. E a tradução de materiais descritos sobre Direito se configura esse passo inicial”, disse Andrea Jane.
De acordo com a coordenadora das Audiências de Custódia, a ação mostra mais uma vez que o Judiciário está antenado às necessidades das populações na inclusão desses povos.
O projeto de acesso intercultural à Justiça, do “Programa Fazendo Justiça”, conta com a atuação conjunta, além do TJAM, Esmam e CNJ, também do Escritório das Nações Unidas sobre Doenças e Crime (UNODC), União dos Povos Indígenas do Vale do Javari (Univaja), Projeto Agro Vida, Museu Magüta, Conselho Indigenista Missionário e Federação das Organizações Indígenas do Rio Negro (Foirn)..
Opiniões indígenas
Pertencente à etnia Kambeba, Melquíades Ventura Neto era um dos indígenas presentes na plateia da 1.ª Conferência Amazônica do Clima e do Meio Ambiente. Natural de uma aldeia do Município de São Paulo de Olivença, no Alto Solimões, ele destacou a iniciativa do CNJ e do Poder Judiciário do Amazonas para com seus parentes das etnias Matis, Kanamari, Marubo e Tikuna.
“A importância desse projeto para os meus outros parentes Marubo, Matis, Kanamari e Tikuna é que ele representa o fortalecimento para nós. Hoje estamos vendo, presencialmente, que há uma preocupação com a língua materna, com a nossa cultura e com os nossos costumes e modo de viver. É muito bom enxergar que a educação se avança em prol de nós, indígenas. Iniciativas como essas nos fazem sentir valorizados pelo Poder Judiciário. Nós sentimos muito felizes por estarem nos enxergando e valorizando a nossa língua materna, trazendo fortalecimento”, declarou.
Para a liderança indígena Marcivana Sateré Mawé, coordenadora da Coordenação dos Povos Indígenas de Manaus e Entorno (Copime), e natural de Maués (distante quilômetros de Manaus), no Baixo Amazonas, a explanação da juíza Andrea Jane sobre os cartazes relativos às audiências de custódia em línguas indígenas no Amazonas “é uma iniciativa muito significativa, uma vez que nesses territórios nos quais estão sendo desenvolvidas essas ações a maioria dos indígenas é falante somente da língua materna nas regiões de Atalaia do Norte, Alto Rio Negro”.
Segundo Marcivana, a ação possibilita que o indígena se faça entender diante daquilo que é questionado. “Então, nos facilita esse entendimento, o diálogo, embora em línguas diferentes. Com certeza é uma valorização para nós, uma vez que um dos grandes desafios que nós temos enquanto indígenas é justamente esse, da vitalização das nossas línguas maternas, e isso só pode ser feito de fato, se fortalecida, com iniciativas como essas, que possamos falar na nossa língua materna, porque é o português que predomina. Além da questão do Direito, também no fortalecimento cultural dos povos”, declarou ela.
Outros paineis
O painel com a juíza Andrea Jane Silva de Medeiros foi antecedido pela abertura do evento por parte do juiz de Direito e secretário-executivo da Enfam, Jorsenildo Dourado do Nascimento e pelos paineis dos palestrantes ministro Herman Benjamin (com a temática “Panorama da Jurisprudência Ambiental do STJ”); Tasso Alexandre Richetti Pires Cipriano (“Logística Reversa e Economia Circular: Desafios e Iniciativas a partir da Agenda 2030”); Tiago Fensterseifer (“O Regime de proteção climática na Constituição Federal de 1988”) e; palestrante Girolamo Domenico Treccani (“Transparência das informações agroambientais na promoção do desenvolvimento sustentável”).
No período da tarde, encerrando o evento, houve grupos de trabalho (GT) enfatizando o “Respeito à autodeterminação dos povos indígenas, comunidades tradicionais e extrativistas e a garantia ao direito à consulta prévia, livre e informada” e “Capacitação continuada e permanente dos agentes de Justiça para atualização e aperfeiçoamento funcional com uso de novas tecnologias e metodologias inovadoras”.
E-books de Morfologia Vegetal ganham versões bilíngues em português e idiomas indígenas no Pará
A iniciativa visa aproximar e valorizar culturas, promover a integração dentro da academia aos monolíngues, que falam apenas a língua portuguesa, com as línguas maternas dos povos originários, fomentando a pluralidade linguística e sociocultural.
Dois e-books elaborados por discentes do Instituto de Biodiversidade e Florestas (Ibef) da Universidade Federal do Oeste do Pará (Ufopa) estão disponíveis para quem tem dificuldade ou curiosidade para entender os termos utilizados na disciplina de Botânica. A novidade é que ambos são bilíngues, em português e idiomas indígenas.
Os e-books, em formato PDF, abordam os conteúdos sobre morfologia da raiz, do caule e da folha. A iniciativa visa aproximar e valorizar culturas, promover a integração dentro da academia aos monolíngues, que falam apenas a língua portuguesa, com as línguas maternas dos povos originários, fomentando a pluralidade linguística e sociocultural.
A apostila ‘Morfologia Vegetal: português e wai wai – Parte 1‘ foi elaborada pelos alunos indígenas Jeremias Xeremias Wai Wai e Lucilene Wai Wai, além dos alunos Andressa Jaqueline Viana de Souza, Jeferson Figueira de Sousa e Alice Gabrielly da Silva Moura, e professoras Cristina Aledi Felsemburgh (disciplina de Botânica no Ibef) e Alanna do Socorro Lima da Silva, ex-diretora do Ibef.
Já a apostila ‘Morfologia Vegetal: português e munduruku – Parte 1‘ foi um trabalho do discente indígena Dinacildo Kirixi Munduruku, também em conjunto com os mesmos alunos e professoras do grupo de trabalho dos discentes Wai Wai.
A disciplina de Botânica está inserida na grade curricular dos cursos de Agronomia, Engenharia Florestal e Bacharelado em Ciências Agrárias da Ufopa.
FONTE: Portal Amazônia
Primeira infância: o desafio da educação indígena
A saga do jovem Puré Juma, do Amazonas, para conseguir estudar é uma síntese do descaso que marca o ensino específico para crianças e jovens indígenas na Amazônia. A falta de estrutura e de material didático mostra que há muita luta pela frente, apesar das conquistas do movimento indígena. Puré, hoje com 20 anos, viu de perto a montagem da estrutura da escola, mas precisou concluir o ensino fundamental em Humaitá (AM). Atualmente, é um dos professores das crianças e lida com a situação precária: goteiras, falta de ventilação, carteiras quebradas e ausência de materiais didáticos. Os povos indígenas lutaram muito pela conquista de uma educação escolar específica e, segundo especialistas ouvidos pela reportagem especial da série “Eleições 2022: Escolha pelas Mulheres e pelas Crianças”, ainda enfrentam o drama de não ter todas as condições previstas em lei.

Puré com sua mãe Borehá Juma e os irmãos Borep, Awipi e Thiago (no colo) (Foto: Odair Leal/Amazônia Real/2014)
LEIA a reportagem na INTEGRA AQUI
FONTE: Amazônia Real